Crude, simple, and disruptive — these words describe DDoS attacks and the overwhelmingly disruptive experience if you get hit. Based on statistics of Infosecurity Magazin, in 2022 E-Commerce projects faced 17% of DDoS attacks with a 53% YoY rise. These attacks are a cause of concern for businesses and users alike as DDoS causes service downtime, financial damage, and operational disruptions.
What is a DDoS attack?
DDoS stands for Distributed Denial of Service. It’s an act where cybercriminals enlist a group of devices — often without the knowledge of the owners — to flood a particular computer with streams of superficial data. This causes the targeted computer to be overwhelmed and prevents it from responding to other legitimate requests.
How does a DDoS attack work?
Cybercriminals launch a DDoS attack through a series of well-calculated steps.
- First, they identify the IP address of the targeted server. Getting hold of the IP address is crucial to ensure the attack hits the right target.
- Then, cybercriminals infect malware into unsuspecting computers. These computers serve as an army of bots — known as a botnet or robot network — that floods the target computer upon the cybercriminal’s command.
- The attacker sends a launch command remotely to the botnet and triggers a collective attack.
- The targeted server is overwhelmed when hit by the DDoS attack and stops responding to regular requests.
Types of DDoS attacks
Yes, there are several forms of DDoS attacks but each has an equally damaging effect on the targeted computer. 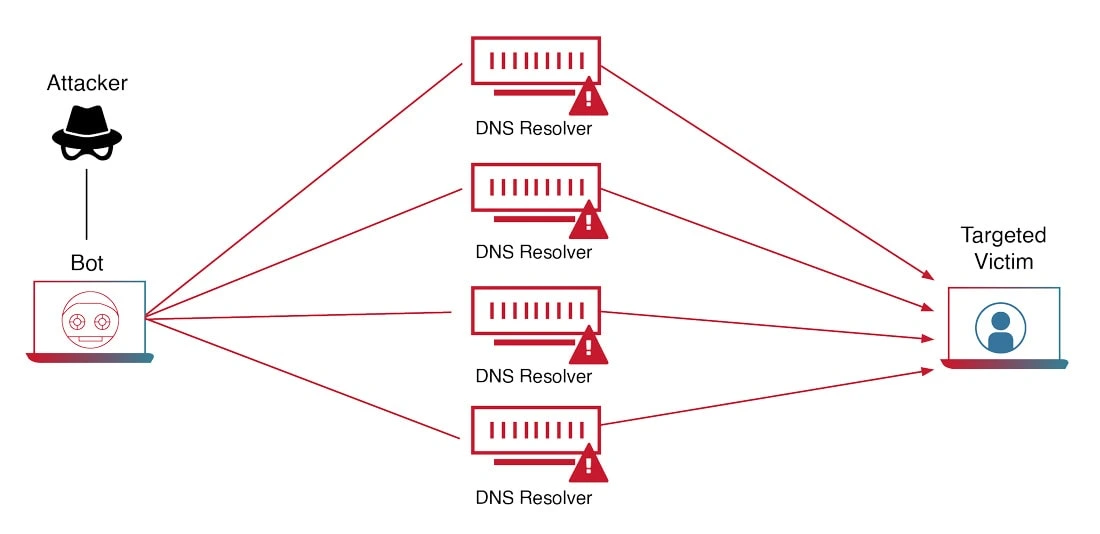
- Volume-based attack – The cybercriminal floods the targeted computer with massive data volumes, eventually consuming the entire bandwidth. The most common types of volumetric attacks are UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol floods.
- Protocol-based attack – This form of attack is designated to exhaust the resources of the target’s network infrastructure. When launched, the attack robs networking components like the firewall and load balancer of the necessary resources to remain functional.
- Application-layer attack – Also known as Level 7 attack, the server is flooded by browser requests, such as repeatedly loading and refreshing a page. Eventually, the server fails to catch up to the increasing request and crashes.
How to prevent DDoS attacks
The purpose of a DDoS attack is to disrupt the operations of a targeted server. The majority of DDoS incidents involve businesses, which calls for the importance of setting up a DDoS mitigation plan for your business. Here are three ways to prevent a DDoS attack in the first place.
Implement cloud redundancy
Always have a backup plan and one of the ways is to have copies of your data, equipment, and systems saved in different locations. With cloud computing, companies can set up redundant servers on the cloud and host them in different physical locations. This ensures the company has ample time to respond to a DDoS attack by switching to the backup server. Also, it pays to choose a scalable cloud architecture that automatically assigns more compute resources as a mitigative measure.
Monitor your network
Monitoring your network is key to preventing DDoS attacks. Signs of an impending attack can be a surge or an abnormal spike of packet transactions, sluggish server performance, and crashes.
Make sure your network security is updated
It’s important that you conduct periodic vulnerability assessments of your internal network to ensure that every endpoint is protected from unauthorized access. It is equally crucial to ensure that the network and underlying computers are secured by the latest anti-malware updates.
How to protect against a DDoS attack
There isn’t a foolproof DDoS protective measure, but you can make it extremely difficult for bad actors to target your computer system. The crux of DDoS protection is to ensure that incoming attacks fail to reach your computer.
You can create basic perimeter protection around the internal network to identify, isolate and block DDoS attacks. Set up a firewall and configure it to block unidentified ICMP packets or DNS requests from unknown sources. This helps to prevent volumetric attacks from crippling the entire system.
Cybercriminals plan DDoS attacks by targeting the victim’s IP address. Therefore, you can spoil their fun by never giving your IP address away. This is where a VPN is effective. A VPN cloaks your computer’s IP address with a commonly-shared IP and prevents the attacker from learning your real IP.
How does VPN prevent DDoS attacks?
A VPN is a networking technology that encrypts data transmission from a computer and ensures anonymity with IP masking. When connected to a VPN, you are protected from possible snooping attempts that could reveal your IP address. The attacker can only see a stream of scrambled information passed from the VPN server to the internet.
You can increase system resilience by using a VPN against DDoS attacks. Some VPNs are built with a kill switch, reducing the opportunities malicious actors can capitalize on to reveal your IP address. A kill-switch is a feature that automatically disconnects the computer from the internet when the VPN connection drops.
How to use a VPN to protect against DDoS attack
Adopting a VPN DDoS protection strategy goes a long way to prevent DDoS attacks. With that said, choosing a VPN provider that demonstrates reliability and a solid record of enforcing user privacy is vital. In that sense, ClearVPN is trusted by businesses for its stellar security performance.
Here’s how to use ClearVPN to safeguard your computer from DDoS attacks.
- Download and install ClearVPN.
- Launch ClearVPN and sign in with your credentials.
- Choose Smart connection shortcut and click Connect Me button.
- Wait for the app to establish a secure VPN connection.
- Computer’s IP address is now hidden, and subsequent data transmission is fully encrypted.
FAQs
Does a VPN protect you from DDoS?
A VPN can offer reasonable protection from DDoS attacks by keeping your computer invisible from the attacker’s radar. Without the computer’s IP address, the attacker can’t launch a DDoS attack. However, a VPN can’t stop an ongoing attack. Neither can it prevent one if the attacker manages to retrieve the real IP address from a backdoor or malware.
Can a DDoS attack be traced?
Tracing the source of a DDoS attack is extremely difficult as it involves the use of an intermediary botnet. Such an effort involves collecting forensic evidence of every event that transpired when the attack was launched.
Can DDoS steal information?
No, DDoS attacks do not steal information from your computer. Instead, the attacker aims to cripple the targeted system or render the website inoperational to other users.
DDoS attacks remain a persistent threat that affects the business community. To prevent these costly disruptions, it’s essential that you improve the security of your network, servers, and connected devices. Adding a VPN to boost perimeter security reduces the risks of DDoS incidences. Download and use ClearVPN to mitigate DDoS attacks now.
