Let’s face it — in today’s digital age, safeguarding personal information and maintaining online privacy have become a paramount concern for everyone. When it comes to enhancing online security, two solutions often come into play — the proxy and the VPN.
While both options offer a way to hide your IP address and protect your online activities, there are significant differences between the two. A good understanding of these differences is essential if we are to make an informed decision about which one is right for us.
Let’s jump in!
Proxy vs VPN: Why does it matter?
First things first — why do you need to understand the difference between a proxy vs VPN? Aren’t they one and the same thing?
Well not at all—and though many may use the terms interchangeably, it’s important to note that they refer to distinct technologies. These differences can significantly impact the level of security and anonymity you have online.
Let’s start with a brief overview of what each one is and how they work. You’ll find that it’s not a matter of one being better than the other, but rather about which one fits your specific needs and online habits.
What is a proxy server?
Without getting too technical, a proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet (hence the name). You can think of it as a middleman, with all your internet requests first being channeled through the proxy’s server before reaching the intended website.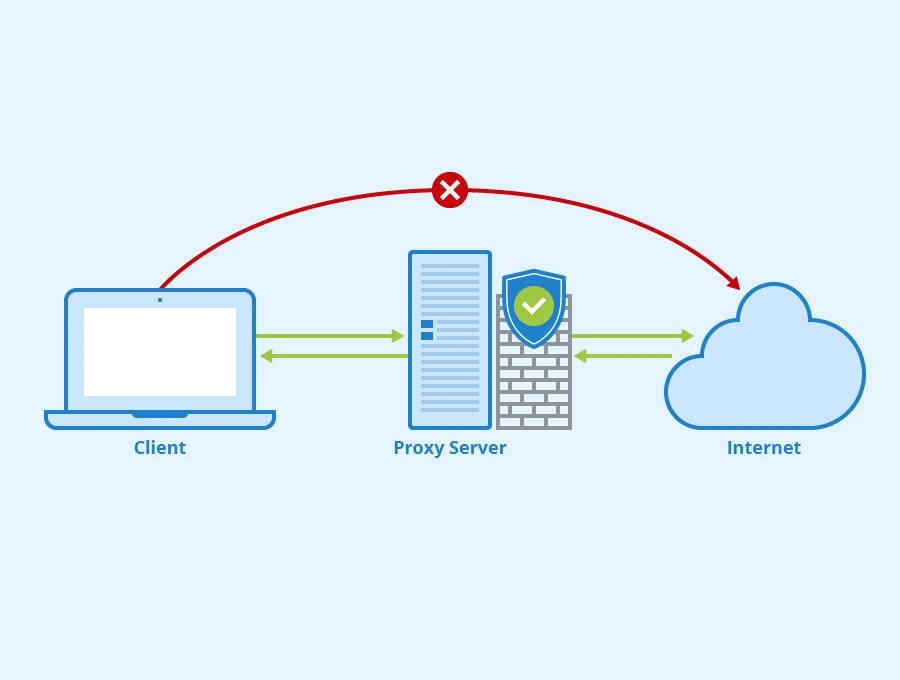
Imagine you are sending a letter to your friend. Instead of mailing it directly, you give it to a friend who is closer to the recipient and ask them to deliver it for you. That is what a proxy server does — it takes your request, masks your IP address and forwards the request on your behalf. The inverse happens when the website responds — it goes through the proxy server before reaching your device, therefore hiding your actual IP address.
What does a proxy do?
There are two main functions of a proxy server — masking your IP address and managing internet traffic.
By masking your IP address, a proxy server allows you to remain anonymous while surfing the web, making it more difficult for websites to track your online activities and determine your location. This can be particularly useful when accessing geo-restricted content or maintaining privacy on public networks.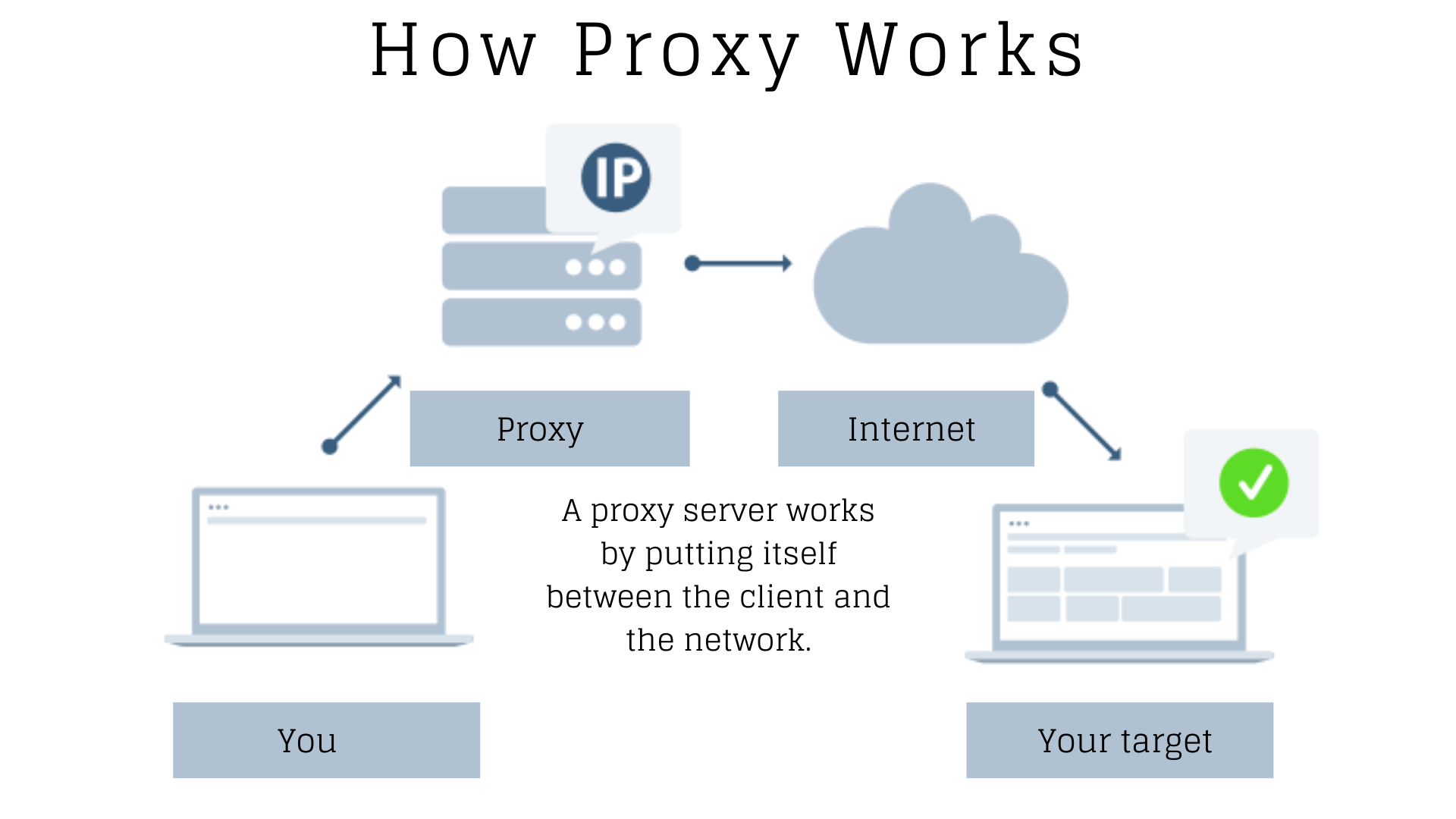
Additionally, proxies can manage and optimize internet traffic. By caching files and reducing bandwidth usage, proxies can shorten loading times and improve performance, especially in large network environments with multiple users. They also provide a measure of security by acting as a barrier between your device and potential malicious resources on the internet, though this is limited due to the lack of encryption (which is where VPNs come in).
What is a VPN?
Now that we’ve covered the basics of the proxy server, let’s take a look at VPNs.
Similar to a proxy, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) also serves as an intermediary between your device and the internet. Importantly, VPNs go beyond the basic function of a proxy by offering an additional layer of security and privacy.
Here’s what we mean by that:
- Encryption: VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making data unreadable to unauthorized parties, providing security for online banking, file sharing, and other sensitive activities, while preventing tracking by hackers or ISPs.
- Tunneling: VPNs create a secure tunnel between your device and destination server, protecting data from external threats and ensuring your online activities remain private and confidential.
Unlike a proxy server, which simply routes your traffic through an intermediary server, a VPN encrypts all the data transmitted between your device and the internet. This means that even if someone manages to intercept your data, they won’t be able to read or decipher it.
Going back to the analogy of sending a letter, imagine that instead of just having your friend deliver it for you, they also put it in a locked box and send it through a secret tunnel to your recipient. That’s essentially what a VPN does by adding an extra layer of security and privacy. The principal difference between proxy and VPN is that a proxy server only hides your IP address, while a VPN also encrypts your data.
What is the difference between a proxy and a VPN?
As we’ve discussed, while both options offer some level of anonymity and allow access to geo-restricted content, they differ significantly in terms of security, functionality, speed, and compatibility.
Let’s recap:
- Functionality: a proxy acts as an intermediary system for managing internet traffic, while a VPN establishes a secure connection with encryption technology.
- Security: proxies provide basic security by acting as a barrier between your device and potential malicious resources on the internet. In contrast, VPNs offer advanced features such as encryption and tunneling to protect data from cyber threats and surveillance.
- Speed: proxies may be faster than VPNs as they do not encrypt data, but this can vary depending on the type of proxy and server location. VPNs may cause some decrease in internet speed due to the encryption process, but this is usually minimal.
Whether you use a VPN or proxy server, one thing remains the same — they both offer a way to mask your IP address and access content that may not be available in your region.
VPN vs Proxy: which one is better?
Much of the debate on VPN vs proxy servers has to do with their different purposes and features. Both can be used to mask your IP address and access restricted content, but they serve different functions when it comes to internet security.
Ultimately, the decision between proxies vs VPN depends on your specific needs. If you simply need basic anonymity or enhanced internet speeds, a proxy might suffice. But if you value security, privacy, and flexibility across multiple devices, then a VPN is probably the better choice.
Getting started with a VPN
The good news is that VPNs have become increasingly affordable and user-friendly these days, making it easier than ever to access the Internet securely and privately. Unlike proxy servers that often require manual setup, many VPNs provide user-friendly interfaces and one-click solutions that can be easily used by anyone, even with limited technical knowledge.
To show you just how easy it can be, here’s a quick guide on how you can get up and running with ClearVPN — a premium VPN service that offers advanced security, privacy and speed for all your online activities.
- Download and install the ClearVPN app on your device. You can do this on a computer (Windows or macOS) or on a mobile device (Android or iOS). If you’re on a desktop/laptop computer, simply go to the ClearVPN website and click on the “Download now” button to download the installer and run it on your device. For mobile devices, you can get the ClearVPN app from the app store of your device.
- Run the ClearVPN app and sign up for an account. A premium subscription starts at $9.99 per month with a free 3-day trial.
- Log on to the ClearVPN app using your account credentials.
- From the dashboard, you can use the quick connect button (big round button in the middle of the app) to automatically connect you to the best server available.
Or you can manually select a specific server location from a list of countries available by clicking/tapping on “Optimal location”.
That’s all there is to it! You’ll find a confirmation from the dashboard that you have established a secure connection along with your new virtual IP address. From here on, all your internet traffic will be encrypted and protected from external threats.
FAQs
Is a proxy better than a VPN?
A proxy offers basic anonymity and potentially faster speeds, but a VPN is better for security by encrypting your data, ensuring privacy, and protecting against cyber threats. If privacy and data protection are priorities, a VPN is generally the better choice.
Can I use a proxy as a VPN?
No, a proxy and a VPN are not interchangeable. A proxy serves as an intermediary for internet requests, offering basic anonymity. A VPN, however, encrypts data and ensures secure, private internet access by creating a protected connection, making it more suitable for safeguarding sensitive information.
Is a proxy cheaper than a VPN?
Yes, proxies are typically cheaper than VPNs, as they offer basic anonymity without the advanced encryption and security features of VPNs. However, the trade-off is a reduced level of privacy and protection, making VPNs worth the extra cost for enhanced security and privacy.
