In today’s hyper-connected world, your choice of web browser can profoundly impact your digital experience. So let’s deeply dive into a comprehensive comparison of two heavyweights in the browser arena — Safari and Google Chrome.
Safari, launched by Apple Inc. in January 2003, was initially designed for Mac OS X and later extended to iOS devices and even Windows (support for which was discontinued after Safari 5). Meanwhile, Google Chrome, launched in September 2008, boasts compatibility with a wider range of platforms, including Windows, Linux, MacOS, iOS, and Android.
This guide will pit Safari against Chrome in a head-to-head battle, scrutinizing the performance of each on both Mac and PC, safety protocols, and other features.
Let’s get cracking!
Google Chrome vs. Safari: A quick comparison
Let’s take a look on a quick comparison table between Google Chrome and Apple Safari:
| Browser | Google Chrome | Apple Safari |
| When Released | September 2, 2008 | January 7, 2003 |
| Engine | Blink (WebKit-based until 2013) | WebKit |
| Platform | Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS | macOS, iOS |
| Speed | Generally considered fast, especially with modern web apps | Known for efficiency and optimization, especially on Apple devices |
| Performance | High performance, but can be resource-heavy, especially RAM | Optimized for Apple hardware, better power efficiency and RAM usage |
| Security | Regular updates, sandboxing, Safe Browsing feature, strong against phishing and malware | Known for strong security on macOS and iOS, built-in fraud warnings, sandboxing |
| Privacy | Offers basic privacy tools, but shares some user data with Google for ad targeting | Strong privacy features, Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) to block third-party cookies |
| Additional Features | – Extensive customizations via Chrome extensions – Synchronization across Google services – Tab management – Integration with Google services | – Integration with Apple ecosystem (iCloud sync, Handoff) – Reader mode- Energy-efficient on Apple devices- Strong focus on privacy features |
Safari vs Google Chrome: breaking it down
Chrome vs Safari Speed Showdown
When evaluating a web browser, speed is of the essence. This becomes especially crucial when loading bulky web pages, streaming HD videos, or juggling numerous tabs. A meticulous comparison by Cloudwards reveals that Google Chrome takes the lead in raw speed. With a score of 122.5, Chrome races ahead of Safari, which clocks in at 113.8.
To put this into perspective, let’s say you’re loading a content-rich website like a news portal or a social media feed. Using Chrome, the site would load approximately 7% faster, saving valuable seconds that accumulate over time.
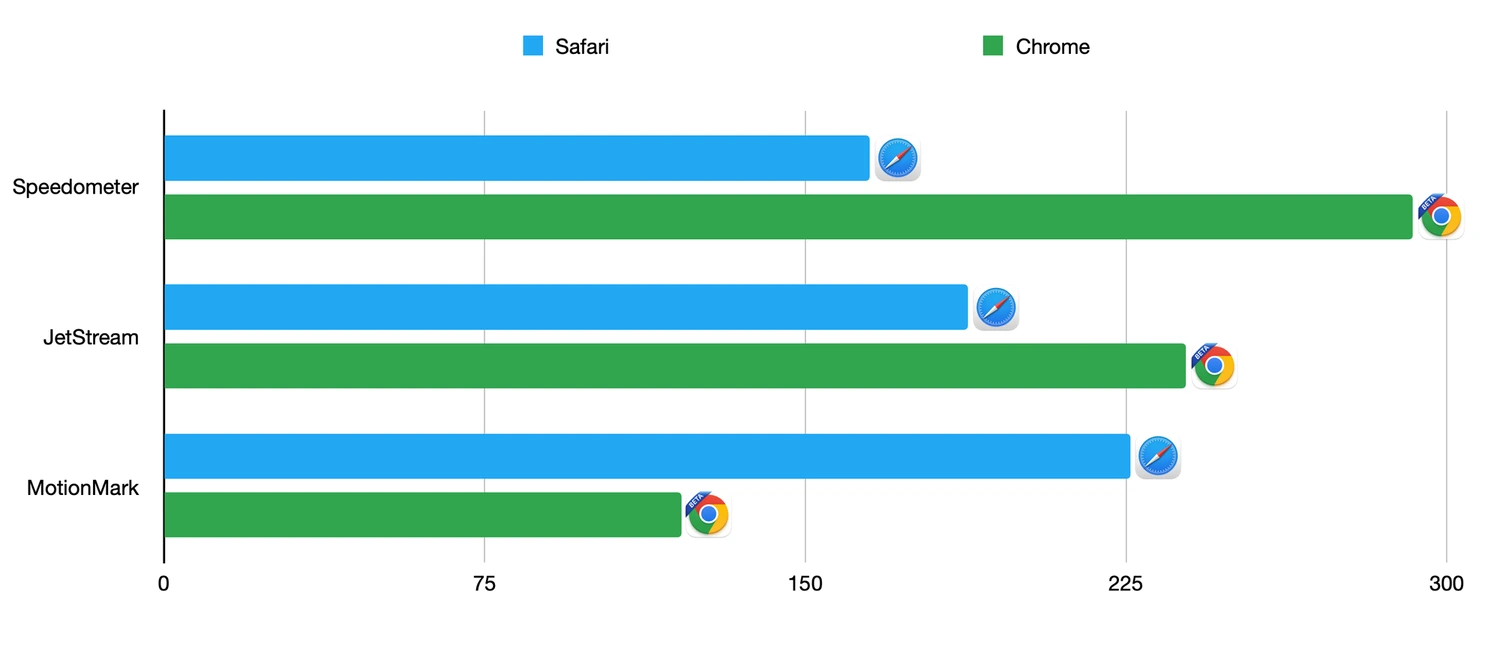
Likewise, if you’re a multitasker who constantly keeps several tabs open — maybe you’re researching for a project, shopping online, and streaming music simultaneously. You’ll notice that Chrome handles multitasking with greater efficiency. Although the difference may seem negligible on a single page, it becomes increasingly apparent as you switch between tabs.
With that said, it’s crucial to remember that speed isn’t simply about rapid page loading. It also encompasses how smoothly the browser operates and its ability to manage demanding tasks. In this aspect, Safari gives Chrome a run for its money. Known for its lightweight design, Safari is engineered to function seamlessly even on older Apple devices.
Safari vs Chrome Performance
Staying relevant in the swiftly evolving tech landscape requires innovation, which is true for web browsers. Safari has consistently proven its adaptability by introducing cutting-edge features in this sphere.
A standout trait of Safari is its flawless integration with the Apple ecosystem. This integration transcends mere syncing of bookmarks and browsing history across devices. For example, if you’re reading an article on your Mac and need to step out, you can effortlessly switch to your iPhone or iPad and resume from where you left off.
Another commendable feature of Safari is its emphasis on user privacy. Its Intelligent Tracking Prevention feature leverages machine learning to identify and block trackers from profiling your online behavior. Safari also syncs with Apple Pay, enabling secure and private online transactions without the need for creating accounts or filling out lengthy forms.
In contrast, while Chrome offers many extensions and add-ons for customization, it lacks the level of device ecosystem integration and privacy features that Safari offers. Chrome’s strength lies in its compatibility with numerous platforms and its widespread adoption, ensuring a consistent browsing experience across various devices.
Safari vs Chrome security showdown
Security is paramount for all internet users. Safari and Google Chrome recognize this and have implemented robust measures to ensure a safe browsing environment.
Google Chrome boasts a suite of security features designed to shield users from various online threats. A key component of Chrome’s security strategy is its sandboxing technology, which isolates each tab and extension within an individual protective shell.
Additionally, Chrome provides a wide range of customizable security extensions, granting users the flexibility to bolster their browser’s security based on personal needs. Chrome also employs Google’s Safe Browsing technology to guard against phishing and malware, alerting users when they attempt to visit dangerous sites or download suspicious files.
Conversely, Safari adopts a slightly different but equally effective approach toward security. By limiting the features and plugins available on its browser, Safari users are shielded from potential exploits. As a result, Safari has historically reported fewer known vulnerabilities than Chrome (according to data from CVE Details), arguably making it safer to use. Also, if you are looking for higher browser security, check our latest detailed guide on top security browsers to use.
Safari vs Chrome privacy
In an age where our digital footprint is increasing and becoming more traceable, privacy has become a significant concern for many internet users. Safari and Chrome have acknowledged this and incorporated features to help safeguard user privacy. However, their approach to privacy differ significantly.
Being a product of the data-centric company Google, Chrome collects substantial user information to personalize the browsing experience and display relevant ads. While this may enhance usability and offer more tailored content, it can raise concerns for users who prioritize privacy.
Chrome does provide several privacy features, such as incognito mode, which prevents your browsing history from being stored on your computer. It also offers options to control cookie tracking and to send “Do Not Track” requests to websites you visit. However, these measures provide only limited protection since trackers can still gather data about your browsing activities.
In contrast, Safari takes privacy very seriously. Apple prides itself on its commitment to user privacy, and this ethos is evident in its browser. Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention feature uses machine learning to identify and block tracking cookies from advertisers, making it much harder for advertisers to target you with personalized ads.
Safari also includes a Privacy Report feature that displays all the trackers it has blocked in the past 30 days, providing a clear snapshot of how it’s safeguarding your privacy. And with iCloud Keychain, Safari can generate, store, and autofill robust, unique passwords, further securing your online accounts.
Read more about Cookies and Cache policy and how to clear Cookies and Cache in Chrome and Safari browsers in our detailed guide here.
Chrome vs Safari: who takes the crown?
So, who wins the browser battle? Safari or Chrome? The answer ultimately depends on your personal needs and your device ecosystem.
If you’re an Apple user who values speed, innovation, and security, Safari might be your ideal pick. But if you prioritize cross-platform compatibility and slightly faster performance, Chrome could be your go-to. Remember, each browser has its strengths and weaknesses. The key is finding the one that aligns best with your browsing habits.
Enhancing privacy and security with a VPN
Regardless of your browser choice, one additional step you can take to boost your online security and privacy is using a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your internet connection, concealing your online activity from ISPs, advertisers, and potential eavesdroppers.
A VPN can also mask your IP address, giving the illusion that you’re browsing from a different location. This is particularly handy if you wish to access blocked or restricted content in your region. Additionally, a VPN provides an extra layer of security when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, often targeted by cybercriminals due to their lax security.
And you can easily start doing that with ClearVPN — a user-friendly VPN with speed and simplicity in mind. ClearVPN offers dynamic server selection, automatically picking the best server based on location and network conditions. Users need only run the ClearVPN app, and click/tap on the main button in the middle of the screen.
Also, ClearVPN doesn’t just secure your digital life but also enhances your online experience. It helps you bypass geo-restrictions, allowing you to access content worldwide, regardless of your location. Whether you’re trying to stream a show unavailable in your country or access international news sites, ClearVPN makes it possible.
FAQs
Is it better to use Chrome or Safari on a Mac?
The answer hinges on your specific needs and preferences. Safari is deeply ingrained with MacOS, offering a smooth and efficient experience. However, Chrome provides a wider range of extensions and cross-platform compatibility.
What’s the difference between Chrome and Safari?
The main differences are speed, security features, and system integration. Generally, Chrome is faster and offers more extensions, while Safari delivers better integration with Apple devices and superior privacy features.
Does Safari include a built-in VPN?
No, Safari doesn’t come with a built-in VPN. However, you can use a separate VPN service with Safari to enhance privacy and security.
